Not a silver bullet but it covers a lot of ground
If you have difficulty connecting your Mac to the internet or keep experiencing slow upload and download speeds, one way to troubleshoot the problem is to reset the macOS network settings to factory defaults. There are three approaches you can rely on to accomplish that.
The first method is the most straightforward and involves the macOS Terminal. In contrast, the second and third methods are slightly complicated and require interactions with the System Settings and Finder apps.
Begin with the Terminal-based network reset procedure in this tutorial. Move onto the other techniques if the network issue you’re troubleshooting persists on your MacBook, iMac, or Mac mini.
Method 1: Reset Network Settings via Terminal
The quickest way to resolve unexpected problems caused by glitchy network settings on a Mac is to shut down and restart the problematic network interface. The macOS Terminal can help you with that.
macOS assigns different physical or logical identifiers to its network interfaces (Wi-Fi, Ethernet, etc.). So, you should first figure out the hardware port of the interface you want to reset.
- Open the Launchpad and select Other > Terminal.
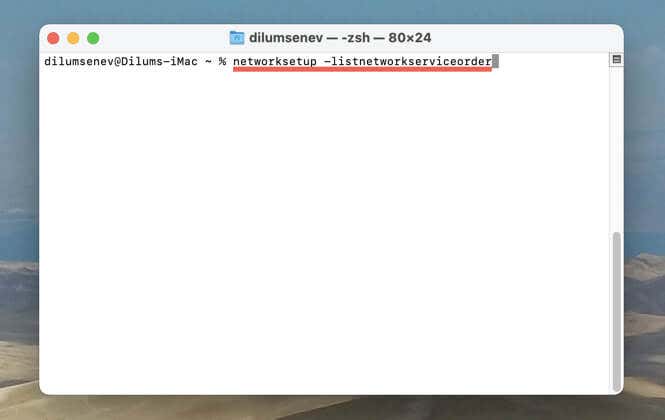
- Run the following command:
networksetup -listnetworkserviceorder
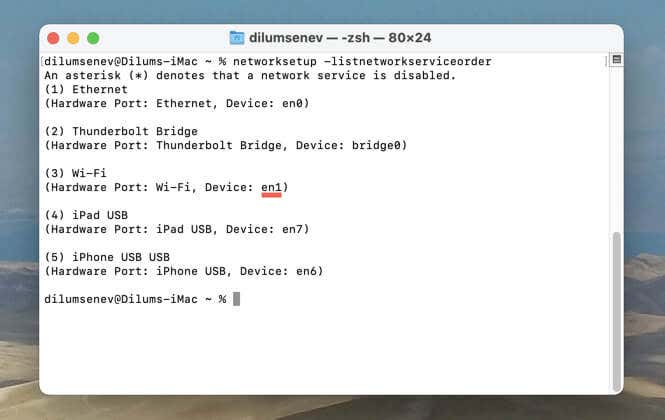
- Note down the hardware port identifier of the interface you want to reset—em0, en1, etc. For example, in the screenshot below, standard Wi-Fi connections use en1 as their identifier.
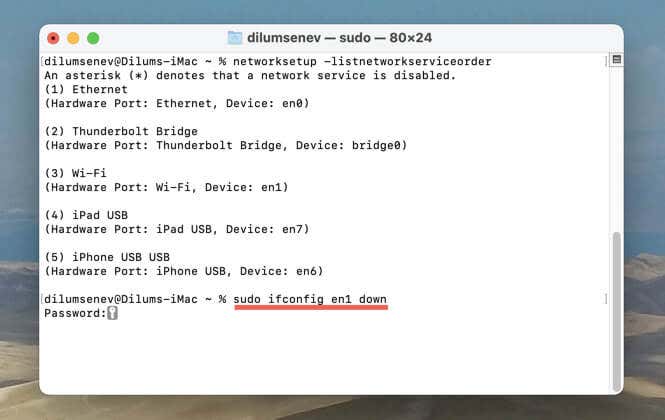
- Run the following command, replacing en0 with the correct hardware port identifier:
sudo ifconfig en0 down
macOS requires you to enter your Mac administrator password to execute the command—just type it out and press Return. The network interface should shut down after you execute the command.
- Run the following command, again replacing en0 with the appropriate hardware port:
sudo ifconfig en0 up
The network interface should reactivate immediately after you run the command.
Method 2: Remove and Re-Add Network Interface
If the Terminal method fails to fix the issue, you must delete and re-add the problematic network interface on your Mac.
If you use a Mac running macOS Ventura or later, you must:
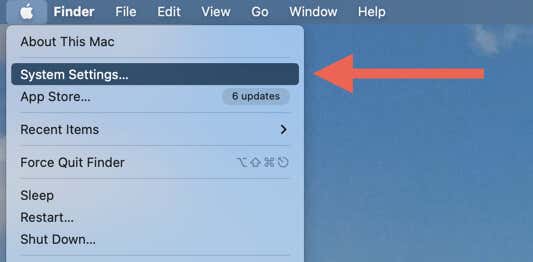
- Open the Apple menu and select System Settings.
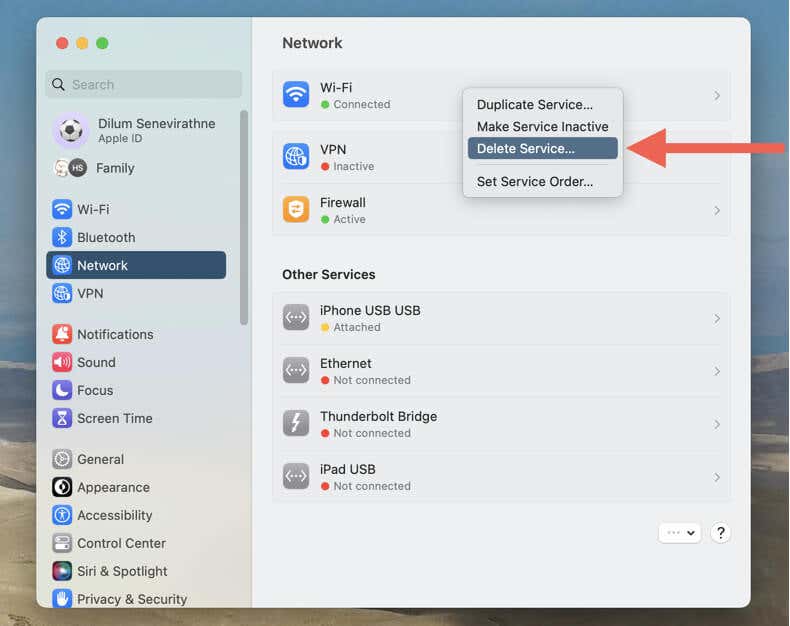
- Select Network on the sidebar. Then, Control-click the interface you want to remove—Wi-Fi, Ethernet, etc.—and select Delete Service.
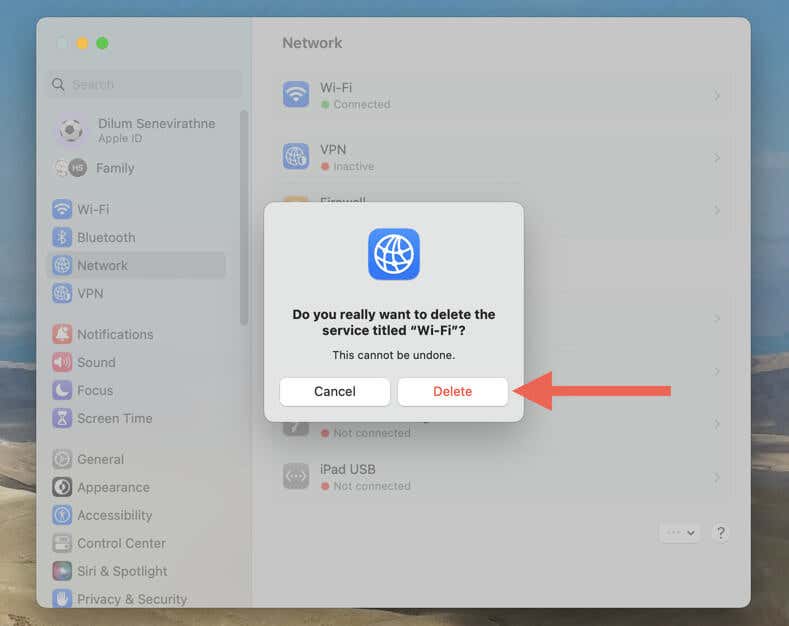
- Select Delete to confirm your action.
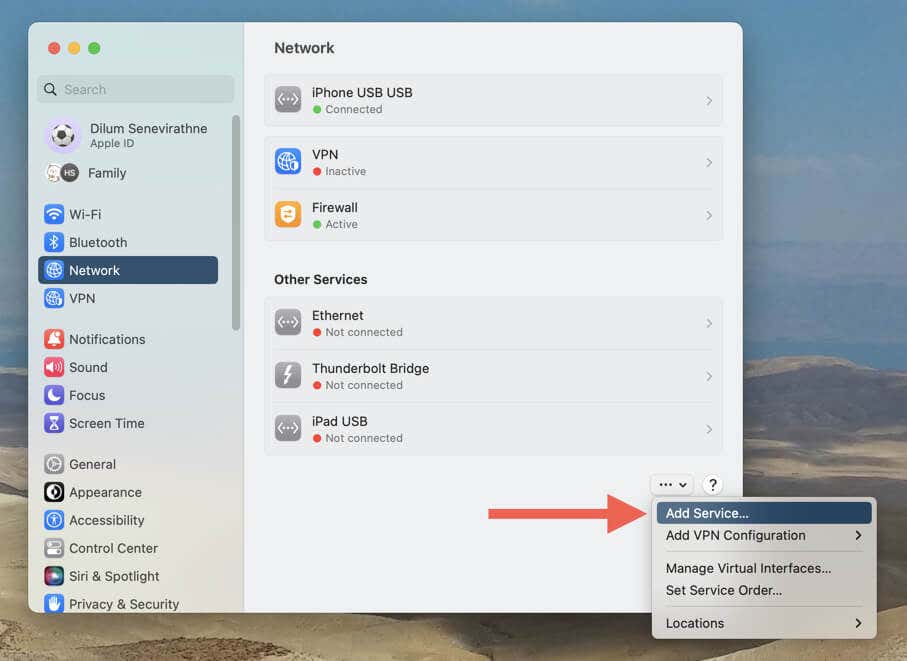
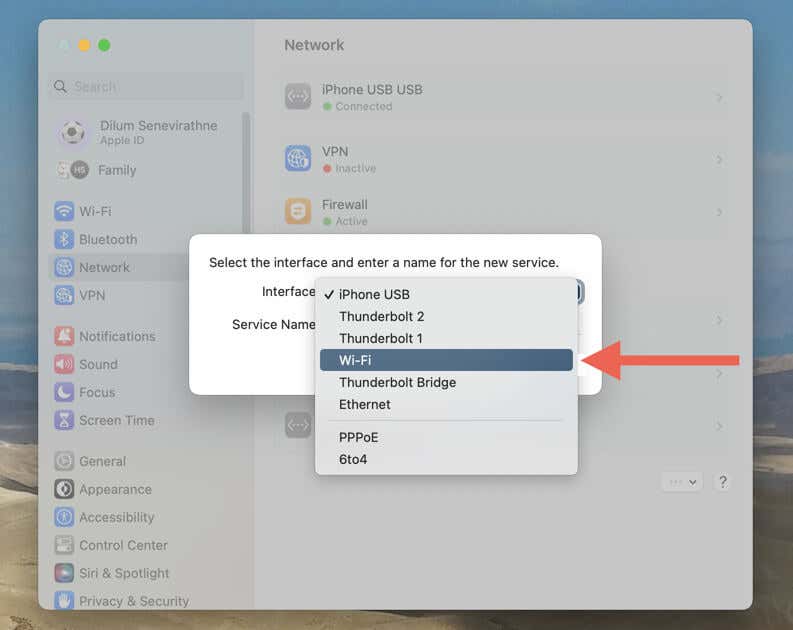
- Select the More icon (three dots) on the lower-right corner of the screen and choose Add Service.
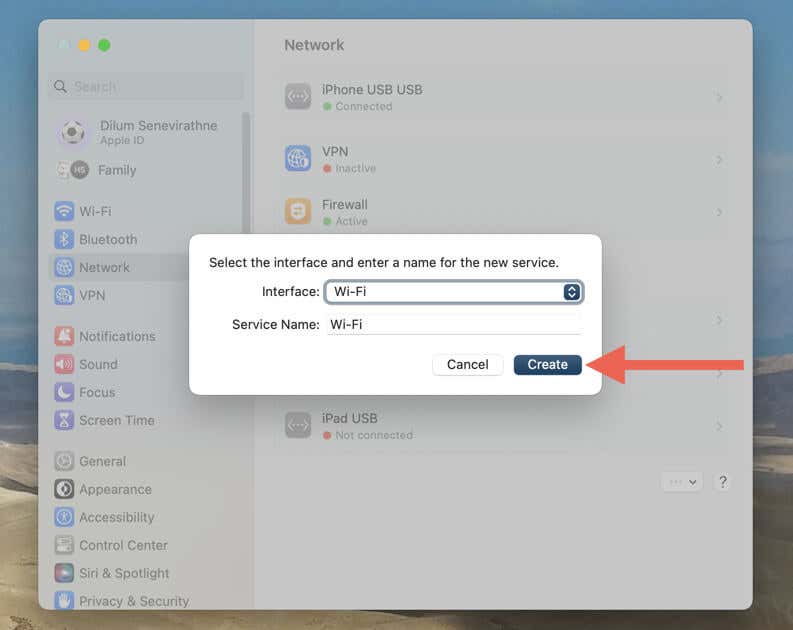
- Open the menu next to Interface and pick the interface you want to re-add, such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
- Select the Create button.
Your Mac should automatically reconnect to available networks once you finish re-adding the interface.
If your Mac runs macOS Monterey or earlier, the steps to delete and re-add a network interface are slightly different due to the user interface changes on the older System Preferences app.
- Open the Apple menu and select System Preferences.
- Select the Network category.
- Highlight the network interface you want to remove.
- Select the Minus icon (lower-left corner of the screen), and then Apply.
- Select the Plus icon.
- Pick the interface you want to re-add—e,g., Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
- Select Create.
Reset Network Settings via Finder
The following method involves deleting your Mac’s network configuration files through Finder, effectively resetting all network interfaces and VPN configurations to factory defaults.
Important: We recommend creating a Time Machine backup before you begin. That gives you the option to roll back any changes in case something goes wrong.
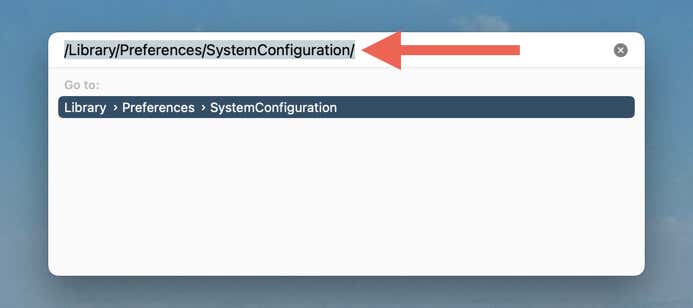
- Open Finder and select Go > Go to Folder on the menu bar.
- Copy and paste the following folder path and press Return:
/Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/
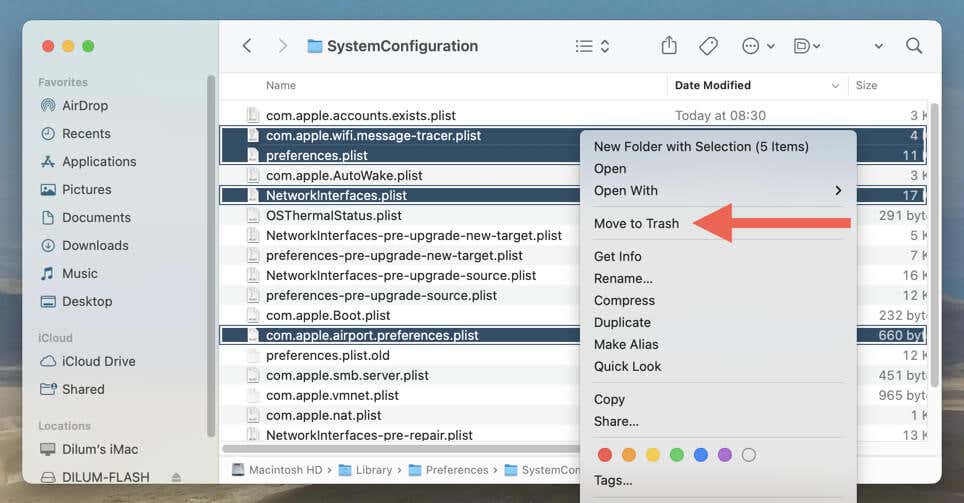
- Control-click the following files and select Move to Trash:
- com.apple.airport.preferences.plist
- com.apple.network.identification.plist
- com.apple.network.eapolclient.configuration.plist
- com.apple.wifi.message-tracer.plist
- NetworkInterfaces.plist
- preferences.plist
Note: Depending on your macOS version, the SystemConfiguration folder may not contain every file above. Just delete the files that are present.
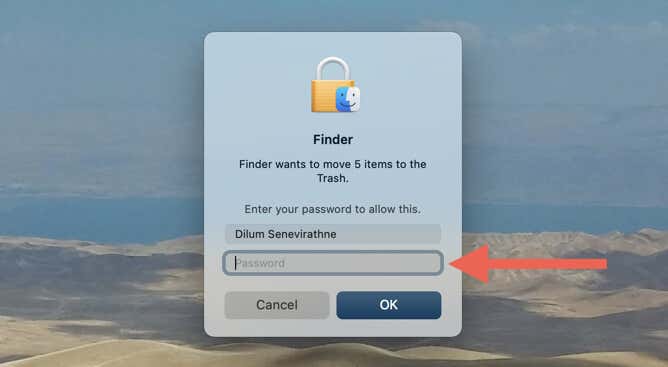
- Enter your Mac user account password and select OK to authorize the action.
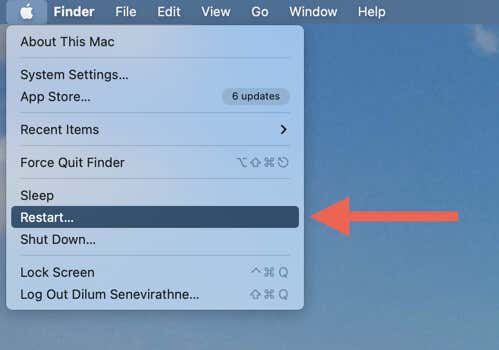
- Open the Apple menu and select Restart.
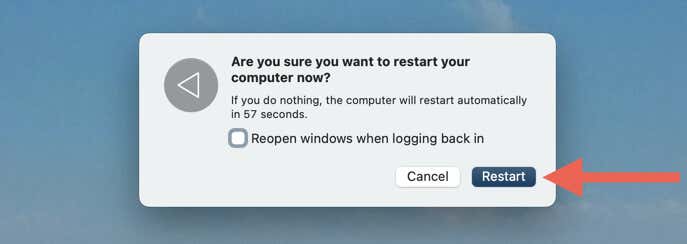
- Uncheck the box next to Reopen windows when logging back in and select Restart again to confirm.
After your Mac reboots, it should automatically recreate the files you deleted. Unlike the previous methods, however, you must manually reconnect to any network afterward.
For example, if you want to rejoin a Wi-Fi network, select the Wi-Fi icon on the menu bar, pick the Wi-Fi name or SSID, and enter its Wi-Fi password.
What Else Can You Try?
A Mac network settings reset aside, there are various standard troubleshooting procedures that can help resolve network-related issues. If you haven’t already, we also recommend that you follow up with the fixes below:
Restart Your Router
Did you know that simply restarting your Wi-Fi or Ethernet router can fix loads of internet connectivity issues on your Mac? Just switch it off, wait for at least one minute, and turn it back on.
If you rely on a mobile hotspot to connect your Mac to the internet, then restarting your iOS or Android device would also help.
Clear the DNS Cache
A corrupt DNS (Domain Name System) cache on the Mac can cause network issues by failing to resolve IP addresses. Run the following command through the macOS Terminal to flush it out:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
Clear the Browser Cache
If network issues occur over a browser only, the web cache is likely obsolete. If you use Safari, here’s how to clear the browser cache:
- Open Safari and select Safari > Clear History on the menu bar.
- Open the pull-down menu next to Clear and select All History.
- Select Clear History to confirm.
Are you using a different web browser? Learn how to clear any browser cache on Mac.
Reset Your Router
This is an advanced fix, but hard-resetting the router is often the best way to address network issues that stem from the router-side.
For comprehensive step-by-step instructions, refer to our guide on factory-resetting a network router.
Network-Reset Your Phone
If the problem occurs over a mobile hotspot, consider resetting the phone’s network settings to its defaults. For example, on an iPhone or iPad, you must:
- Open the Settings app and select General.
- Go to Transfer or Reset iPhone/iPad > Reset.
- Select Reset Network Settings.
Mac Network Settings Reset Successful
A network settings reset isn’t the silver bullet to all connectivity issues that occur on a Mac computer. Still, it does cover a lot of ground in your troubleshooting attempts. Make sure to research the nature of the problem and work on any additional fixes to resolve the issue. You can also contact Apple Support or your internet service provider for extra help.